Beyond Functionality: Exploring the Emotional Dimensions of UX/UI Design
While functionality and usability are essential in UX/UI design, they are not the only factors that determine the success of a product. At 365CREA, we believe in the power of Emotional Design—crafting experiences that resonate emotionally with users. This article delves into the emotional dimensions of design and how they can elevate user experiences to new heights.
What is Emotional Design?
Emotional Design is the practice of creating digital products that evoke emotions in users. It’s about designing interfaces that go beyond mere functionality to create an emotional connection with the user. Whether it’s joy, trust, or a sense of accomplishment, these emotions can significantly enhance the user experience.
The Benefits of Emotional Design
- Increased User Engagement: Products that evoke positive emotions are more engaging. Users are more likely to spend time on a product that makes them feel good.
- Improved User Retention: Helps build strong connections with users, leading to increased loyalty and retention.
- Enhanced Brand Perception: A product that resonates emotionally can elevate a brand’s image, making it more memorable and likable.
Principles of Emotional Design
- Human-Centered Design: It all starts with understanding the human element. Designers must consider users’ needs, emotions, and behaviors.
- Aesthetic Usability Effect: Attractive designs are perceived as more usable. By focusing on aesthetics, designers can create products that are not only functional but also visually appealing.
- Consistency: Consistent design helps build trust and reliability, leading to positive responses.
Designs Elements That Evoke Emotions
Key elements such as color, typography, and imagery play a significant role in evoking emotions:
- Color: Colors have a profound impact on emotions. For instance, warm colors like red and orange can evoke feelings of excitement and urgency, while cool colors like blue and green can create a sense of calm and trust. Understanding color psychology is essential in creating designs that resonate with users.

Color
- Typography: The choice of fonts can also evoke specific emotions. Serif fonts like Times New Roman can convey a sense of tradition and reliability, while sans-serif fonts like Helvetica are often perceived as modern and straightforward. The size, weight, and spacing of text can further influence how users feel about the content.

Typography
- Imagery: Visuals such as photographs, illustrations, and icons can evoke strong emotions. Images of happy people, for example, can induce feelings of joy and positivity, while minimalist illustrations might convey simplicity and clarity. The right imagery can reinforce the emotional tone you want to set.

Imagery
The Three Levels of Emotional Design
Emotional design operates on three distinct levels, each contributing to how users perceive and interact with a product:
- Visceral Design: This is the first impression users get when they see a product. It’s about the immediate emotional reaction to the visual aesthetics. Visceral design focuses on making a product visually appealing to trigger an emotional response, such as attraction or curiosity.
- Behavioral Design: This level is about the usability and functionality of the product. It’s where the emotions related to user satisfaction, ease of use, and efficiency come into play. A product that functions smoothly and meets user needs creates positive behavioral emotions.
- Reflective Design: Reflective design is about the long-term emotional connection users develop with a product. It’s influenced by personal memories, brand associations, and the overall impact the product has on the user’s life. Reflective design fosters loyalty and attachment, turning users into advocates for the brand.
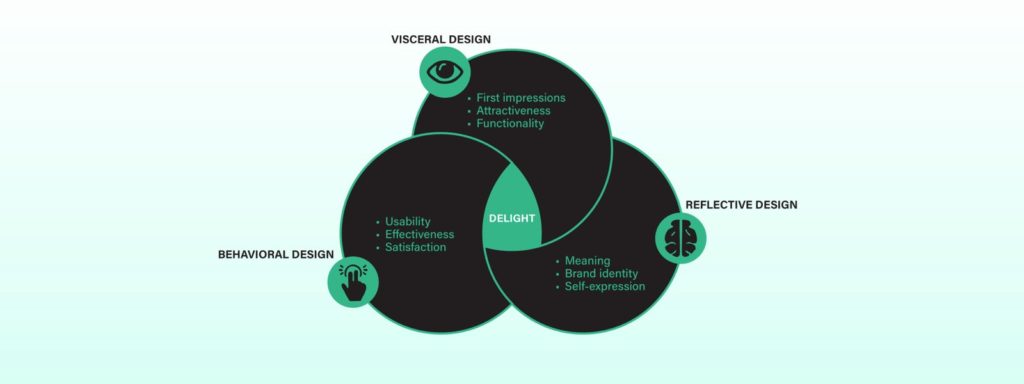
Three levels of Design
Case Studies in Emotional Design
- Google’s Minimalist Approach: Google’s clean and simple design fosters a sense of calm and focus, making the user experience efficient and pleasant. This is evident in products like Google Search, where the uncluttered interface keeps users focused on finding information quickly.

[google.com]
- Patagonia’s Ethical Storytelling: Patagonia’s website and app designs highlight their commitment to sustainability, evoking emotions of trust and responsibility in their users.

Source: [https://www.patagonia.com/home/]
- Spotify’s Personalized Experience: Spotify uses data-driven personalization to create playlists and recommendations that resonate emotionally with users, making their experience unique and enjoyable.

Source: [https://open.spotify.com/]
Implementing Emotional Design in Your Projects
- Understand Your Audience: Conduct research to understand what emotions your users are seeking. Tailor your design to meet those emotional needs.
- Incorporate Feedback: Regularly collect and analyze user feedback to understand the emotional impact of your design. Use this data to make improvements.
- Balance Emotion with Function: While emotions are important, functionality should not be compromised. Strive for a balance where emotional design enhances, rather than detracts from, usability.
At 365CREA, we strive to design experiences that connect with users on a deeper level, ensuring that our products are not just used, but loved. As we continue to push the boundaries of design, Emotional Design will remain at the forefront of our approach, helping us create meaningful and impactful user experiences.

13 comments
discount androxal usa overnight delivery
August 16, 2025 at 5:14 pmbuying androxal cost without insurance
get androxal generic in united states
buy enclomiphene price australia
August 16, 2025 at 5:19 pmbuy cheap enclomiphene buy hong kong
how to buy enclomiphene for sale usa
online order rifaximin uk delivery
August 17, 2025 at 2:12 amrifaximin canada free sample
get rifaximin cheap united states
buying xifaxan generic drug india
August 17, 2025 at 2:20 amget xifaxan cheap real
get xifaxan cost per tablet
buy staxyn generic cheap
August 17, 2025 at 3:47 ampurchase staxyn uk cheap purchase buy
buy cheap staxyn cheap where
how to buy avodart non prescription online
August 17, 2025 at 3:47 ambuy cheap avodart uk online pharmacy
avodart discount
get dutasteride cheap usa
August 17, 2025 at 5:07 ambuying dutasteride generic when available
get dutasteride without prescriptions uk
online order flexeril cyclobenzaprine generic efficacy
August 17, 2025 at 5:07 amhow to buy flexeril cyclobenzaprine price generic
how to order flexeril cyclobenzaprine cheap with fast shipping
discount gabapentin generic new zealand
August 17, 2025 at 6:01 amorder gabapentin price london
ordering gabapentin purchase england
kamagra levné
August 17, 2025 at 7:04 amnejlevnější místo na nákup kamagra online
kamagra konzultovat s lékařem
medicament kamagra acheter bon marche
August 17, 2025 at 7:37 amgenerique kamagra pharmacie au rabais comtat venaissin
acheter kamagra en montreal
fildena next day
August 17, 2025 at 2:56 pmget fildena buy hong kong
how to order fildena uk meds
canadian itraconazole prices
August 18, 2025 at 2:31 amdiscount itraconazole on line
how to order itraconazole price in canada
Comments are closed.