AI-Driven Personalisation and Design: Transforming the User Experience Landscape
Personalisation in design has long been sought after, but only recently has it been reshaped through the capabilities of Artificial Intelligence (AI). Rather than relying on static user journeys or broad demographic assumptions, user experiences are now being tailored dynamically—driven by data, behaviour, and machine learning algorithms.
How AI is Shaping Personalised Experiences
Through behavioural tracking and pattern recognition, interfaces are being adapted in real time. Layouts, colour schemes, and even content types are being adjusted based on user interaction data. This adaptive model ensures that every user is met with an experience that feels intuitive and relevant—without requiring manual configuration from design teams.
Instead of offering a single, universal design, interfaces are being fine-tuned to respond to each user’s preferences. For example, content modules might be reordered based on past clicks, or a navigation menu could be simplified for someone consistently engaging with just a few features. These subtle yet powerful modifications are being made possible through AI-driven decision engines.
Personalisation in design has long been sought after, but only recently has it been reshaped through the capabilities of Artificial Intelligence (AI). Rather than relying on static user journeys or broad demographic assumptions, user experiences are now being tailored dynamically—driven by data, behaviour, and machine learning algorithms.
Understanding AI-Driven Personalisation
AI-driven personalisation is powered by deep learning models, natural language processing (NLP), and predictive analytics—technologies that are being applied to analyse behavioural patterns, historical activity, and contextual signals. A structured process is typically followed to deliver such tailored user interfaces:
- Data is being collected and preprocessed from multiple touchpoints, such as browsing history, demographics, purchase behaviour, and device usage. This raw data is then anonymised and structured to meet privacy and compliance standards.
- Patterns are being recognised and user profiles clustered using machine learning. Users are being grouped into behavioural segments based on preferences and interaction history.
- Content is being adapted in real time, where reinforcement learning techniques and live analytics are used to adjust layouts, recommend content, and alter UI components dynamically.
- Feedback loops are being maintained, allowing the AI models to evolve continuously. Metrics such as session duration, click-through rates, and engagement are being used to refine future personalisation efforts.
This dynamic and iterative cycle allows user interfaces to stay relevant and engaging while minimising cognitive load.
Real-World Applications of AI-Driven Personalisation
AI-powered design is not a theoretical concept—it is already being applied by industry leaders:
- Netflix uses AI to personalise both content recommendations and thumbnail images. Depending on a user’s past viewing habits, different visuals are shown for the same movie or series. This helps increase engagement and click-through rates.
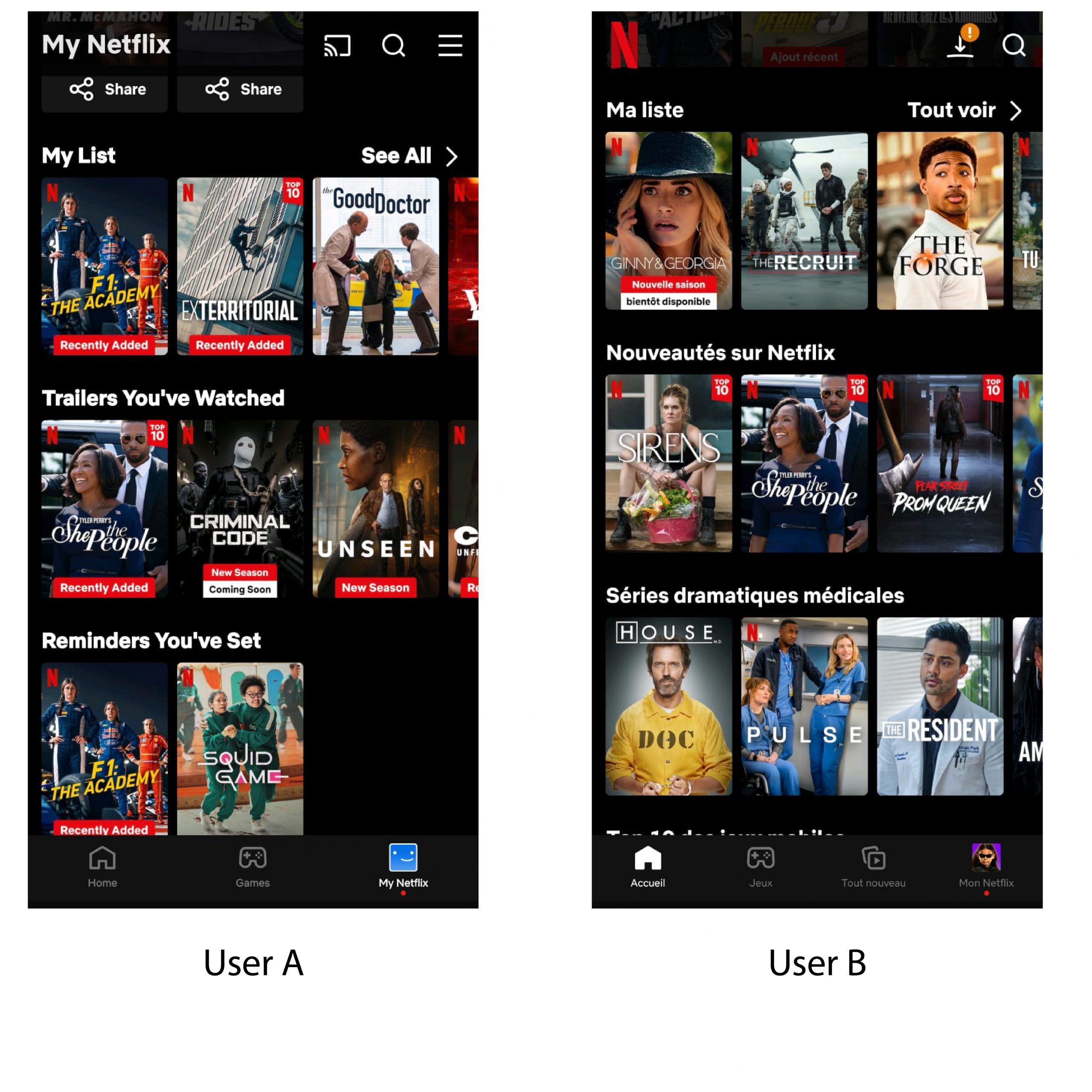
Netflix tailors its interface based on user behavior and preferences — as seen here, User A and User B have unique layouts, categories, and content suggestions to enhance their personalized streaming experience
- Spotify offers personalised playlists like “Discover Weekly” and “Daily Mix,” generated through deep learning algorithms that analyse listening history, song characteristics, and user mood patterns.
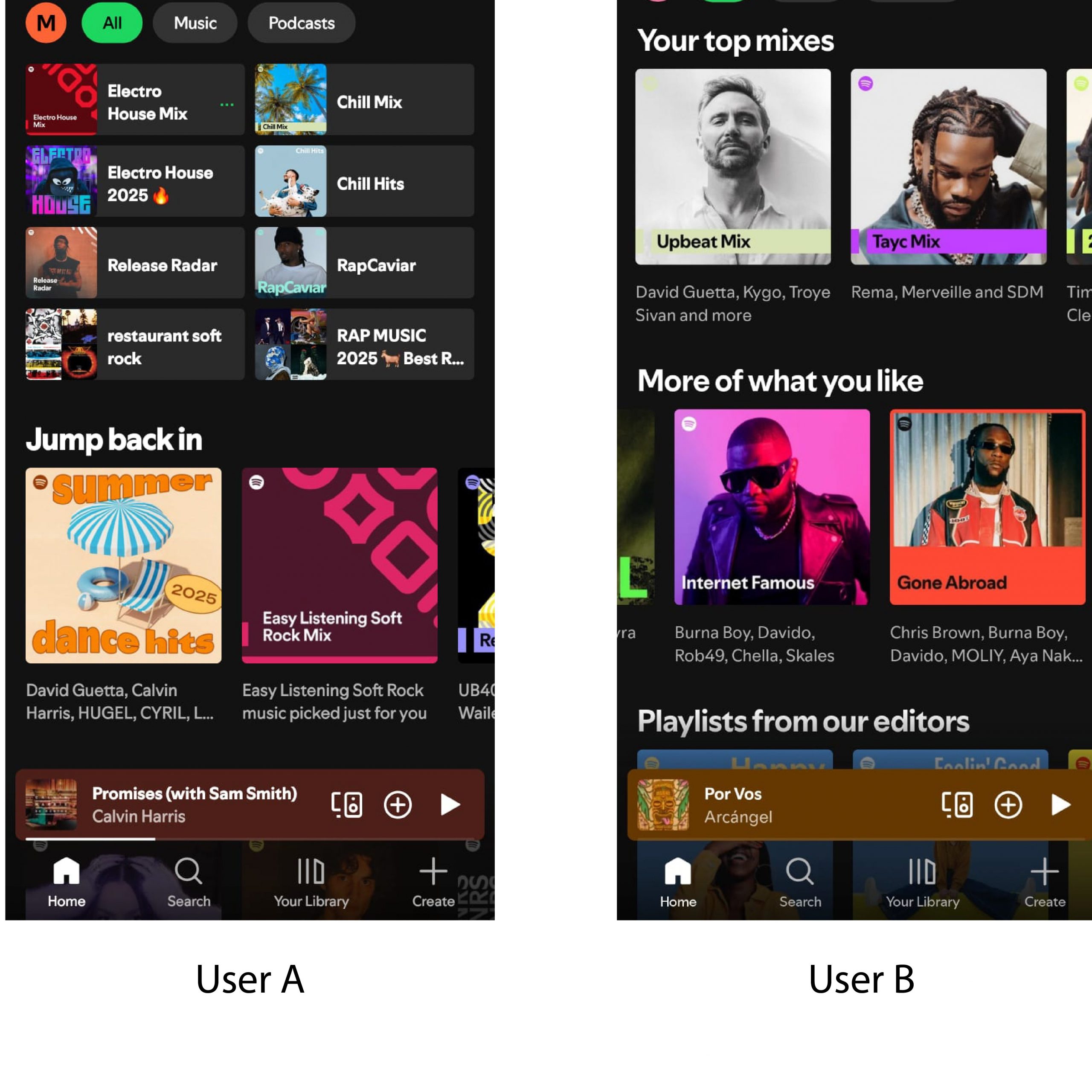
Spotify recommends tracks based on users preferences or listening time in that genre
- Amazon tailors its homepage, product recommendations, and even pricing suggestions based on browsing behaviour, purchase history, and device usage—enhancing the shopping experience for millions.
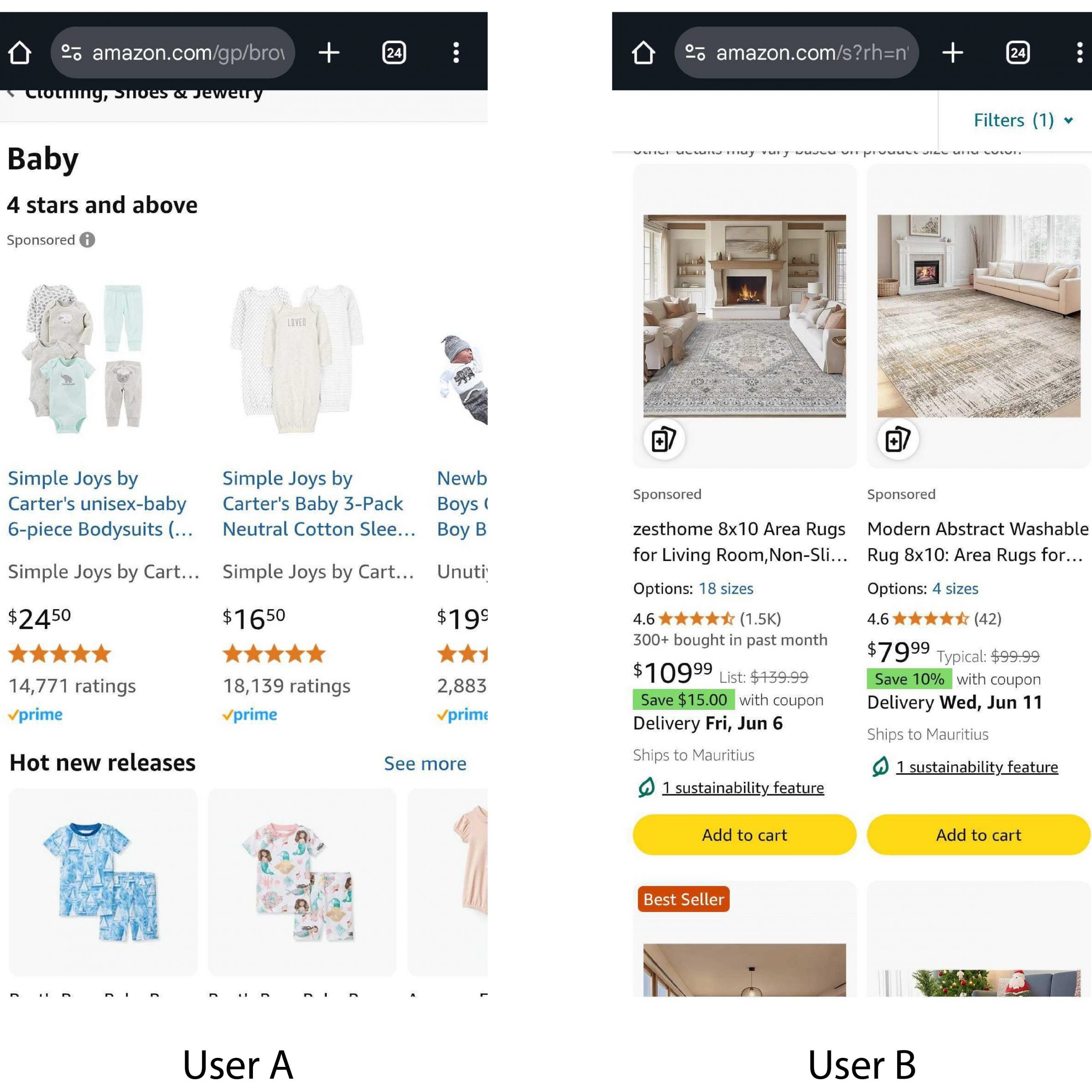
Amazon curates this list from User A’s past purchases
The Role of Predictive Analytics in UI Design
Predictive analytics is being used to forecast user behaviour before it occurs. By examining historical usage data, interfaces are being empowered to anticipate user intent and present options preemptively. This proactive strategy minimises friction and strengthens user satisfaction—two key indicators of successful design.
As a result, user journeys are being transformed from reactive click paths into anticipatory experiences designed to feel seamless and efficient.
Dynamic Content and Modular Design
AI has also influenced the shift toward modular, component-based UI systems. Rather than building rigid templates, design systems are now created to be fluid and interchangeable. Each component, such as a call-to-action, banner, or form, can be shown or hidden depending on the user’s profile or intent.
This modular flexibility is being used to deliver truly unique experiences at scale, with AI acting as the curator behind the scenes.
Ethical Considerations and Balance
While AI-driven personalisation offers numerous advantages, ethical design practices must be prioritised. Transparency in data use and respect for privacy must be maintained. Users should feel guided, not manipulated.
A balance must be struck between automation and intentional design. Decisions must not be left entirely to algorithms—human-centred thinking must remain the foundation.
A Shift in the Role of Designers
With AI handling much of the adaptation and personalisation, the designer’s role is evolving. Rather than crafting one-size-fits-all experiences, designers are now focusing on system thinking—creating frameworks and logic that allow AI to personalise effectively.
Empathy and storytelling are still essential, but they are being applied differently—by designing the logic that lets machines deliver human-like interactions.
At 365CREA, AI-powered personalisation is being explored not only as a trend but as a standard for digital experience. As interfaces become smarter, every click, scroll, and pause is being used to deliver design that feels effortless and made-for-you.
Design is no longer static. It is being continuously shaped—by intelligence, by data, and most importantly, by the user.

13 comments
Online consultation for androxal
August 16, 2025 at 4:55 pmorder androxal buy virginia
discount androxal generic when available
ordering enclomiphene canada mail order
August 16, 2025 at 4:57 pmindianpharmaonline enclomiphene
how to buy enclomiphene price south africa
ordering rifaximin buy online canada
August 17, 2025 at 1:54 amcheapest buy rifaximin generic india
buy rifaximin overnight free delivery
how to order xifaxan generic side effect
August 17, 2025 at 1:58 amnon prescription cheap xifaxan
order xifaxan uk cheap purchase buy
buy staxyn canada cost
August 17, 2025 at 3:25 ambuy staxyn canada medicine
cheapest buy staxyn buy adelaide
discount avodart generic medications
August 17, 2025 at 3:25 amorder avodart cheap wholesale
Cod avodart
buy dutasteride new york city
August 17, 2025 at 4:44 amhow to buy dutasteride australia suppliers
discount dutasteride uk sales
buy flexeril cyclobenzaprine where to purchase
August 17, 2025 at 4:44 ambuy flexeril cyclobenzaprine generic is it legal
online order flexeril cyclobenzaprine generic ingredients
how to order gabapentin toronto canada
August 17, 2025 at 5:42 amgabapentin price canada
cheapest buy gabapentin usa mastercard
buy cheap fildena us pharmacies
August 17, 2025 at 5:47 amordering fildena generic united states
order fildena canada how to buy
itraconazole overnight delivery saturday
August 17, 2025 at 6:37 amorder itraconazole generic cheapest
ordering itraconazole generic is it legal
kamagra na lince bez lékařského předpisu
August 17, 2025 at 6:42 amkamagra nejnižší ceny
kanadské léky kamagra
sans ordonnance kamagra en spain
August 17, 2025 at 7:20 amgénérique kamagra pas cher au canada
sera kamagra aider faible testosérone
Comments are closed.